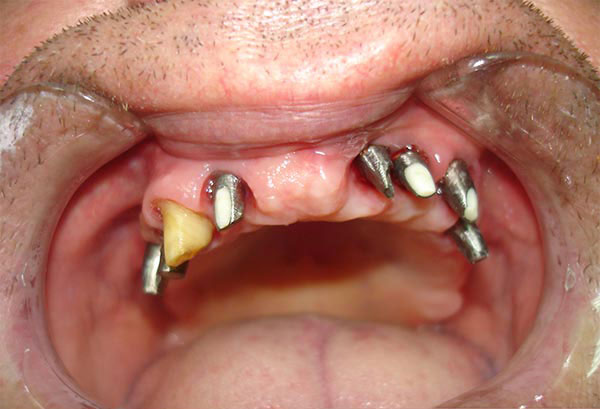
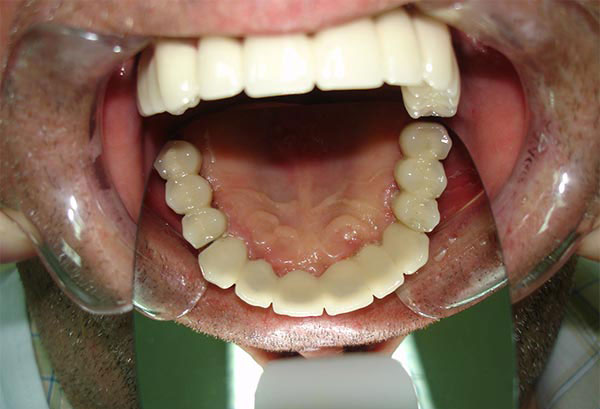
Dental prosthetics
Dental prosthetics deals with the planning and production of prosthetic restorations, respecting the following requirements:
- funcionality;
- resistance;
- security;
- aesthetics.
Dental prosthetics is a specialist area of dentistry that, in simple terms, enables the return of lost teeth.
In this branch of dentistry, a high-quality dental laboratory, which accompanies the dentist and closely cooperates with him, is of essential importance.
How doest he tooth loss occur?
Tooth extraction can occur through the traumatic eruption of a tooth from the alveolar cup (fight, fall, accident), as well as due to periodontitis and chronic infections in the jaws. However, in most patients tooth loss occurs due to long untreated deep caries.
What are the consequences of tooth loss and why is dental prosthetics so important?
Tooth loss leads to various anatomical and functional disorders, but also to aesthetic changes on the face.
The lack of a large number of teeth is the cause of the shortening of the lower mass of the face, that is, the displacement of the lower jaw bone.
In addition, the bone in the place where the teeth are missing is resorbed because the physiological stimulation that the teeth once produced is missing. Bone resorption or lack of bone will later require jawbone augmentation for the installation of dental implants.
Moreover, the teeth located opposite the place of the missing tooth begin to migrate because there is no longer a counterforce that keeps their position stable.
In addition to these anatomical problems, a number of problems with chewing and digesting food also occur.
Fortunately, dental prosthetics allow toothless people to regain their health, self-confidence and smile widely again with the help of various dental restorations.
What types of prosthetic replacements does dental prosthetics include?
Dental prosthetics is divided into fixed and mobile and foresees the application of the following prosthetic compensations:
-
- crown;
- inlay, onlay and overlay;
- facet (veneer);
- implants;
- bridges;
- prosthesis.
Fixed dental prosthetics
Fixed dental prosthetics includes fixed works that are permanently cemented or screwed in the mouth, and the patients cannot remove them on their own.
The prosthetics deals with the production of crowns and bridges, extensions, inlays, onlays and other dental restorations that are permanently fixed in the mouths of patients.
Which compensation the prosthetic rehabilitation of the jaws will be achieved with, depends on many factors.
These can be the following:
-
- reduced jawbone volume;
- mandibular nerve condition;
- periodontopathy;
- jaw trauma;
- jaw cysts;
- jaw tumors;
- other diseases of jaws and teeth.
Based on a clinical examination by a specialist in prosthetics, oral surgery and implantology, i.e. jaw orthopedics, history and images of teeth and jaws (X-ray, CT, CBCT), the most effective method of prosthetic therapy is determined.
Crowns - Metal-ceramic and metal-free (ceramic)
In dental practice, there are several types of crowns and dental bridges, but their fundamental division includes:
-
- metal-free (ceramic);
- metal-eramic.
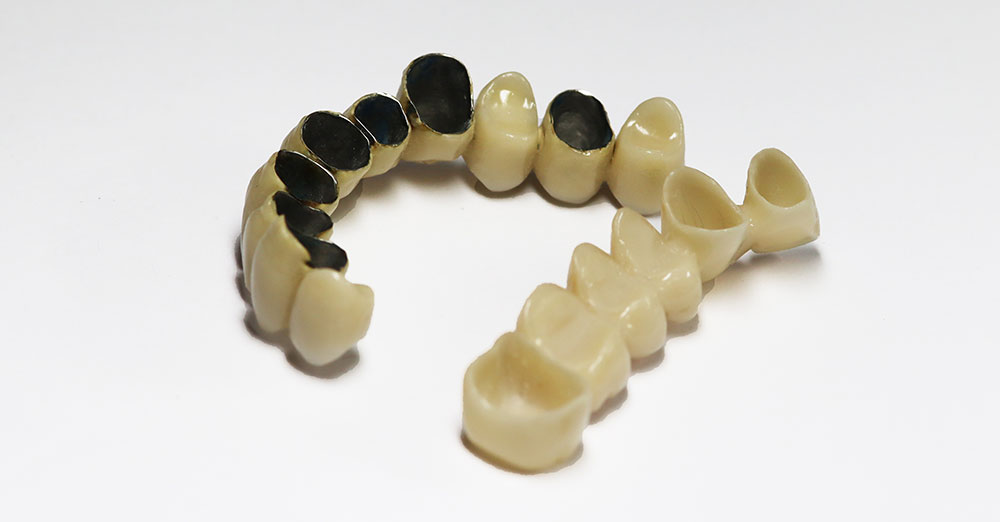
Metal-Ceramic Crowns: These crowns are made from biocompatible metal alloys, with a surface layer of ceramics or porcelain. They are used for complete or partial fixed prosthetic work (circular bridge), in combined prosthetic work (supporting removable dentures), and in implant prosthetics.
Metal-free crowns or zirconia crowns are increasingly popular today. First of all, this is because the edge of the metal-free crown is extremely precisely formed, because the technology of computer scanning and zirconium base production is used in their production. This provides high accuracy and precision of the edge of the crown, so perfect contact is achieved between it and the gums.
Also, the material from which the crown is made is biocompatible and does not cause irritation of dental tissue. Modern production technique enables high polishing without microcracks, which prevents the formation of dental plaque.
Zircon-ceramic crowns are therefore chosen by patients who strive for superior quality and aesthetics.
Where conditions exist, crowns are placed on existing ground teeth. However, in the case of toothlessness, the fitting of crowns is conditioned by the installation of implants.
Advantages of this material:
- High biocompatibility;
- Non-abrasiveness;
- Non-porosity;
- Irreplaceable aesthetics;
- Exceptional strength;
- Absence of metals;
- Durability;
- Skeletal prosthesis.
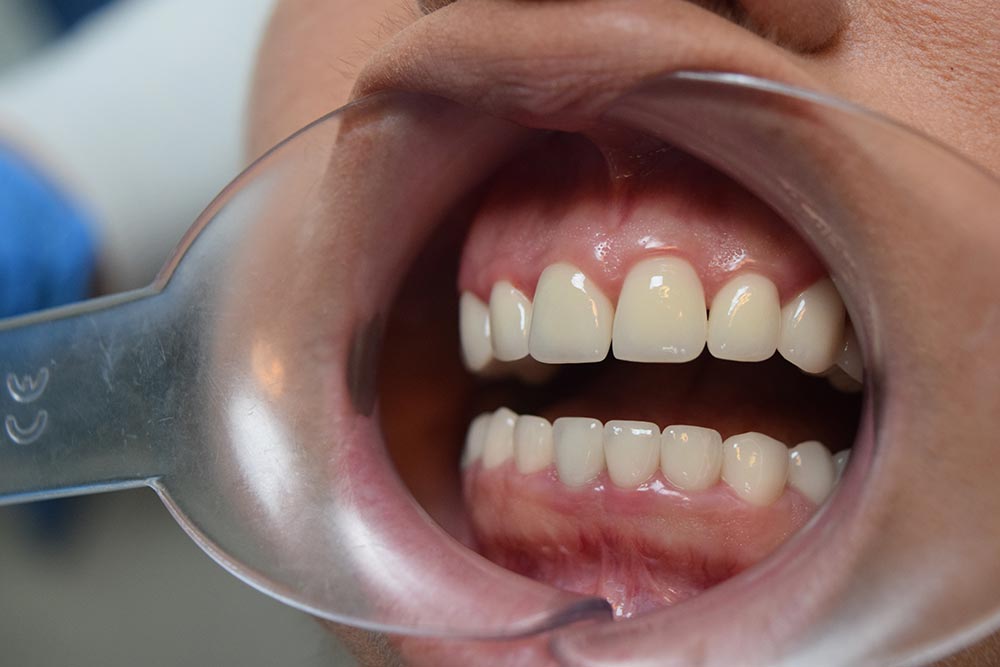
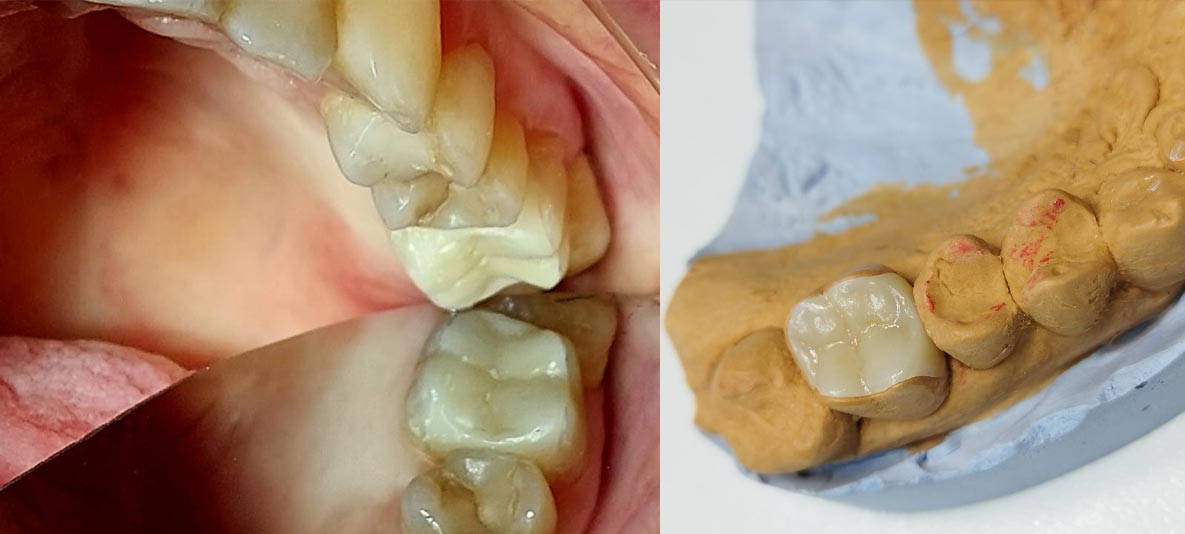
Inlay, onlay and overlay
Inlay, onlay and overlay also belong to fixed dental prosthetics and serve to reconstruct the crown of the tooth.
Carious lesions are known to cause damage to teeth. When the cavity is removed, a space called a cavity is created in that place. When part of the dental tissue is missing, it can be compensated with a composite filling or a ceramic inlay or onlay.
The difference between these two restorations is in the method of application and the size of the dental tissue that needs to be replaced.
When the entire biting surface of the tooth is covered, a filling in the form of an onlay is required. If the filling is smaller and does not cover the entire chewing surface, it is called an inlay.
The technology of making inlays in dental technology is very similar to making covers (crowns) for teeth. The inlay is formed by taking an impression so that it perfectly matches the created cavity. It is then glued to the tooth with a special cement.
This prosthetic replacement is made of ceramic, composite or gold. Most patients opt for a ceramic inlay, mainly because of the excellent quality-price ratio, i.e. economy.
The color of the ceramic inlay is adjusted to be identical to the color of the natural tooth. This type of restoration does not change color over time and is a more long-lasting solution than fillings. For the production of inlays, the cooperation of a specialist in dental prosthetics with a dental laboratory is required.
Ceramic inlay is very resistant to fracture, withstands pressure very well and does not require restoration for 20-30 years.
Ceramic facets (veneers)
By placing veneers, many aesthetic defects on the teeth can be easily corrected. Facets or veneers are used to correct the color and shape of the teeth, various damage to the enamel, closing the diastema (gap) between the front teeth, minor defects and visible fillings. Veneers are thin flakes, 0.3–1.3 mm thick, which are placed mainly on the front teeth. They can be made of composite material, ceramic or zirconium. Depending on the manufacturing material, the installation technique, durability and price of the veneer differ.
Facets made of composite material are placed directly in the patient’s mouth, while those made of ceramic and zirconium are made in dental laboratories. Ceramic facets are far more durable, while composite facets must be replaced every few years. Also, there is a risk of ceramic cracking. In this case, a new facet must be made.
The main reason why patients choose ceramic facets more often than ceramic crowns is that the teeth are ground less and only the outer surface of the teeth is damaged.
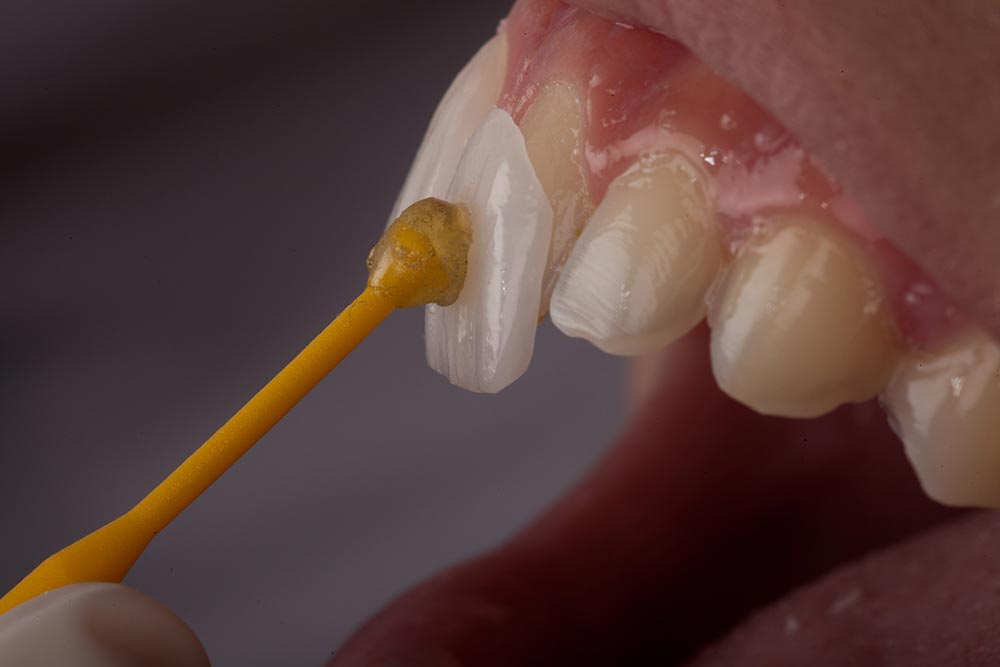
NO-PREP veneers
NO-PREP veneers ( no preparation, without preparation) are veneers that are installed without prior grinding of the teeth.
These veneers are directly attached to the tooth that has been thoroughly cleaned and treated with special preparations.
This method is painless, the patient does not feel any discomfort, and veneers glued in this way can last up to 10 years.
Dental prosthetics and dental implants
Dental implants are titanium or zirconium screws, which are implanted in the jawbone and grow with it over time.
When the fusion process (osteointegration) is completed, the crown is placed on the abutment (the part that connects the crown to the implant). In this way, the natural appearance of the jaws and their full functionality is achieved.
This means that patients who have undergone implantology chew food, speak and smile as if they had their own teeth.
Dental implants are titanium or zirconium screws, which are implanted in the jawbone and grow with it over time.
When the fusion process (osteointegration) is completed, the crown is placed on the abutment (the part that connects the crown to the implant). In this way, the natural appearance of the jaws and their full functionality is achieved.
This means that patients who have undergone implantology chew food, speak and smile as if they had their own teeth.
Dental bridges
If the patient is missing several teeth, a bridge is recommended. Dental bridges are attached to the existing, ground teeth and bridge the toothless parts of the jaws.
This type of restoration is placed on two or more healthy teeth, if they are able to support the bridge.
The advantage of dental implants compared to bridges is that there is no need to grind adjacent, healthy teeth during implant installation.
Mobile prosthetics
Mobile prosthetics refers to movable (non-fixed) prosthetic restorations, which the patient can remove and wash himself.
This type of compensation includes:
-
- classic acrylate total and partia prostheses;
- prostheses on implants;
- valplast prostheses.
Classic acrylate total and partial prosthesis
This type of prosthesis is one of the more affordable dental replacements, which are used in partially or completely toothless patients. With their help, the functionality of the jaws and the beauty of the smile can be preserved in a simple and economical way. Their only drawback is that they require a longer period of adaptation, which is conditioned by their relative bulkiness.
Based on an individual impression taken in the office and without prior preparation (grinding) of the remaining teeth, they are made of acrylate in pink color.
When making a partial acrylic prostheses, several tests are carried out, and the color of the artificial teeth is matched to the color of the patient’s teeth.
Partial acrylate prosthesies are fixed to adjacent teeth using special metal hooks, while total prostheses firmly adhere to the jaw thanks to the creation of a vacuum between the prostheses and the alveoli.
Skeletal Dentures
Skeletal (vizil) dentures, or dentures with a metal framework, represent an improvement compared to traditional acrylic dentures because the metal framework provides better and more precise adherence to soft tissues.
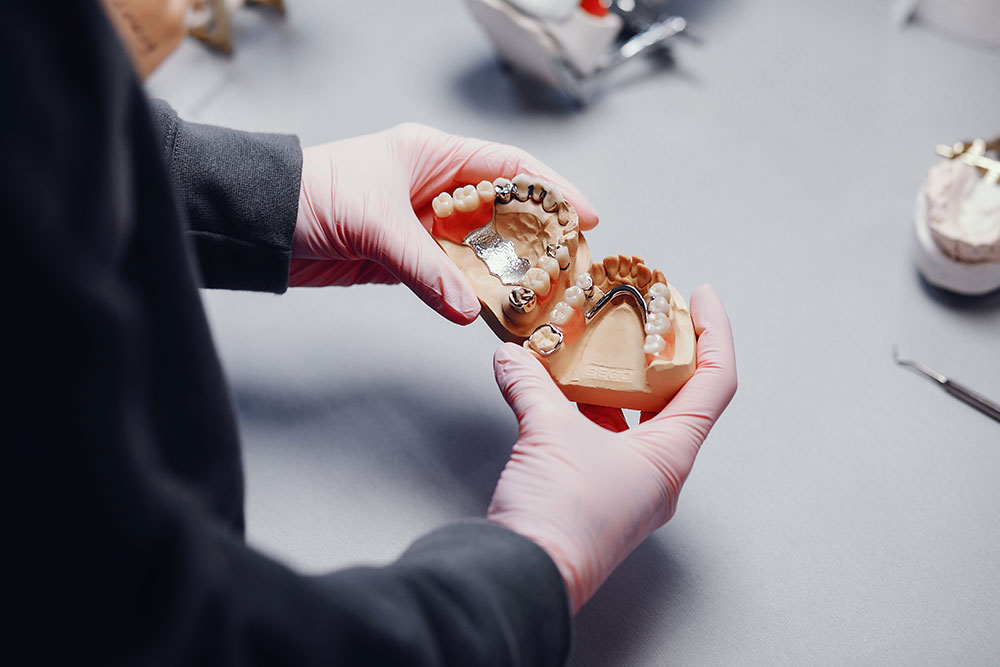

These dentures are used when there is a lack of lateral teeth in the jaw, making it impossible to create a dental bridge. In addition to the mentioned advantages, they are more durable as prosthetic replacements and are more cost-effective compared to dental implants.
Prostheses on implants
If the patient is faced with the lack of all teeth in one or the other jaw, the cost-effective solution is total prosthese that are placed on implants.
Prostheses on implants are known as all-on-4 because they involve the installation of four implants in the toothless jaw.
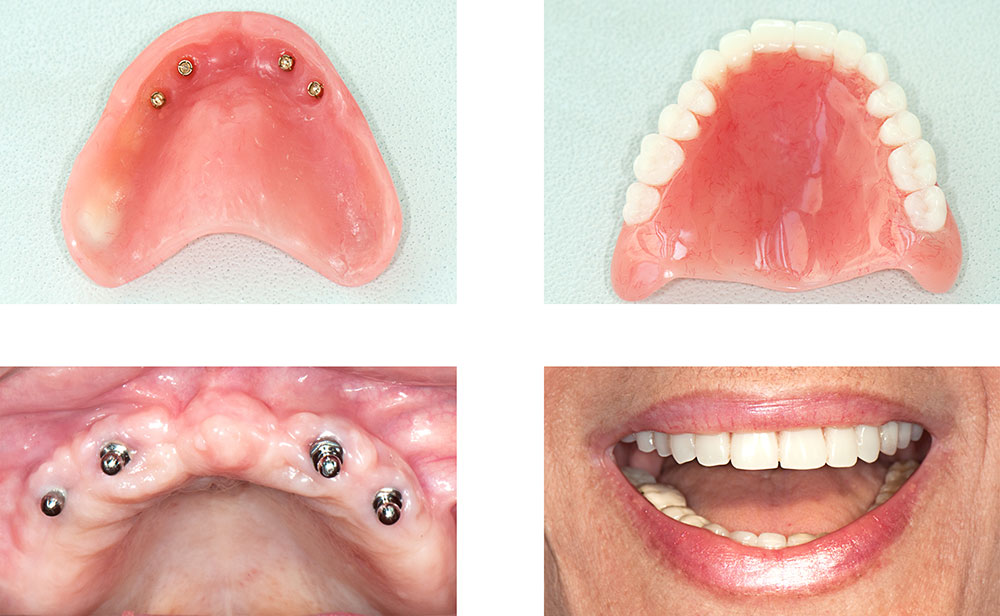
Prosthesis on implants works according to the Driker system. This means that locators are first placed on the implants, and then the prosthesis is fixed, which fits perfectly on them.
The prosthesis on the implants is fixed and provides greater comfort when speaking and chewing than a classic, mobile prosthesis. Therefore, it is considered more practical and safer.
Valplast prostheses
If for some reason it is not possible to place implants and bridges, the best solution is a mobile total valplast prosthesis.
This flexible silicone prosthesis is highly adaptable and long-lasting. It is made of biocompatible, thermoplastic silicone material, which is hypoallergenic and reacts to body temperature. This makes it more adaptable to jaws.
These prostheses are smaller in size compared to classic ones, but this is not a source of problems in their daily use. On the contrary, with valplast, there are no disturbances in speech and chewing.