Periodontology
Periodontology is a field of dentistry whose subject is the peridontium and soft tissues of the oral cavity. The peridontium refers to the supporting structure of the tooth (gingiva, cementum and alveolar bone).
Why is periodontology important?
Periodontology deals with conditions and diseases that affect the mentioned tooth structures, trying to restore and preserve their health.
The good condition of the gingiva (gums) significantly affects the longevity of the teeth and the perfection of the smile. That is why modern dentistry pays special attention to comprehensive gum health – an aspect known as pink aesthetic.
How does periodontology treat periodontal disease?
The diseased supporting apparatus of the teeth is subject to two types of therpy:
- causal;
- surgical.
Causal periodontal therapy
Kauzalna parodontološka terapija podrazumijeva sljedeće postupke i ciljeve:
- removal of hard and soft dental deposits (ultrasound and manual instruments);
- treatment of periodontal pockets;
- establishment of adequate occlusal-articulation relations of the teeth;
- restoration of carious lesions;
- treatment of some general diseases.
Surgical therapy
Causal periodontal surgical therapy includes the following interventions:
- gingivectomy and gingivoplasty;
- mucogingival surgical procedures (frenectomy, apically displaced flap, expansion of the attached gingival zone and deepening of the vestibule);
- modified flap operation according to Widmann.
In emergency situations, adequate urgent therapeutic measures are applied to the supporting apparatus of the teeth. They include the drainage of periodontal abscesses and the use of antibiotics.
Periodontology - Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why do my gums bleed?
Gums bleed as a result of inflammation. Inflammation of the gums occurs due to inadequate hygiene and the presence of a large amount of hard and soft deposits on the teeth. Bleeding gums is an alarm to visit the dentist.
2. Why are my teeth loose?
Teeth are most often loose due to inflammation and loss of the jawbone, the cause of which is periodontitis.
3. Why are my gums receding?
There are several factors that influence receding gums: the presence of tartar, inflammation of the gums, mucogingival anomalies, etc.
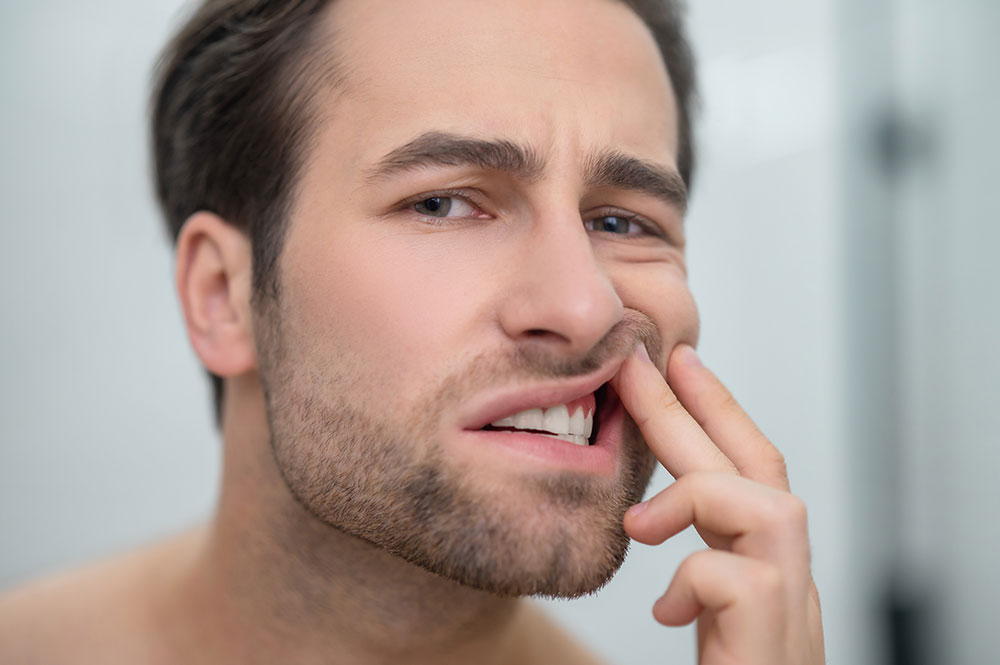

4. Why do the necks of my teeth hurt when I’m cold?
Teeth can hurt on cold stimuli due to receding gums, when the cementum of the tooth remains exposed, and it otherwise shows extreme sensitivity to cold.
5. Why do I have bad breath?
The presence of periodontal pockets most often leads to unpleasant breath due to the accumulation of bacteria and their products in the space around the teeth.
Periodontal pockets are the most important sign of periodontal disease. They can also arise as a result of inappropriate contacts between fillings or inadequate prosthetic work.
Periodontology and periodontal treatments
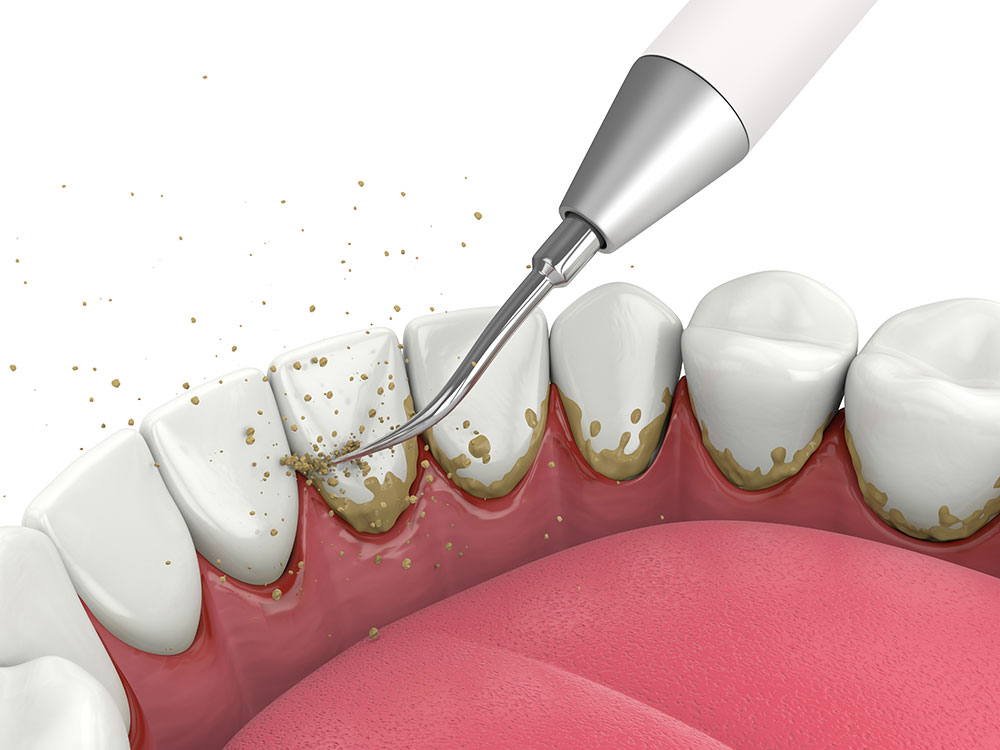
The first step towards preventing problems with the gums and teeth is to remove tartar (plaque).
5 reasons to remove tartar
If you’re not sure why it’s important to remove tartar regularly, read these five reasons:
- Solving the problem of bad breath. By removing tartar, you will significantly improve the appearance of your teeth, while getting rid of bacteria that cause bad breath.
- Maintaining good oral health. During regular dental check-ups (every 6 months), caries or possible inflammatory processes can be detected and treated in time.
- Gum disease can be stopped. By removing tartar, the progression of gum disease is prevented.
- Prevention of periodontosis (periodontal disease).
- Achieving a beautiful smile. Frequent consumption of colored drinks and smoking leave pigments on the teeth. By removing tartar or polishing your teeth, your smile becomes irresistible.
Periodontology and implantology - A new method of soft tissue treatment Endoret® (PRGF®)
Platelet rich plasma (PRP) therapy is a new method of treatment that involves the application of growth factors and proteins from the patient’s blood plasma.
This method is used with the aim of promoting faster wound healing and tissue regeneration after oral surgery, periodontology and implant surgery.
Apart from periodontology, oral surgery and implantology, this method is also used in aesthetic medicine.
Four biocompatible PRP formulations in dentistry
- Endoret® (PRGF®) SUPERNATANT is used for infiltration directly into the alveolus or into the bone to stimulate cell growth.
- LIQUID Endoret® (PRGF®) is used for infiltrations in dermatology and sports medicine, as well as in dentistry for immersion of implants for better osseointegration.
- CLOUT Endoret® (PRGF®) is used for filling defects and bone regeneration, and can be mixed with autologous or artificial bone.
- FIBRIN MEMBRANE, due to its hemostatic properties, is the best material for covering defects and encouraging epithelization, and it can remain exposed.
Why is PRP so important in dental procedures?
The progress of oral surgery and other dental branches often implies the application of materials and procedures that contribute to the improvement of clinical results.
Stem cell-enriched plasma (PRP) is a modern approach for tissue regeneration. PRP is widely used in various surgical fields, including head and neck surgery, otolaryngology, cardiovascular surgery, and maxillofacial surgery.
Usually, PRP is used in a gel formulation, which is formed by mixing PRP (created by centrifuging one’s own blood) and thrombin and calcium chloride. PRP gel contains a high concentration of platelets and fibrinogen.
Platelets are a rich source of important growth factors. During wound healing, they will be among the first cells to respond to wounds, which is important for initiating the regeneration process.
Recently, PRP has become a valuable adjunct to promote healing in many oral surgery procedures
In such procedures, the natural stickiness of PRP allows easier handling of the graft material. This includes gluing artificial bone with more predictable hap-adaptation and hemostasis – stopping bleeding and a predictable seal on the wound. This is the main advantage of using PRP in terms of the primary healing of the wound itself.
Therefore, the goal of using PRP is to find a treatment that could reduce bleeding, promote high-quality bone and soft tissue regeneration, and thus speed healing. The use of this tool is simple, and its price is more than economical.
